Neuron Activation in Artificial Neural Networks
[Neuron Activation-Function Artificial-Neural-Networks Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
A artificial neural network (ANNs) is network of neurons which are interconnected between layers.
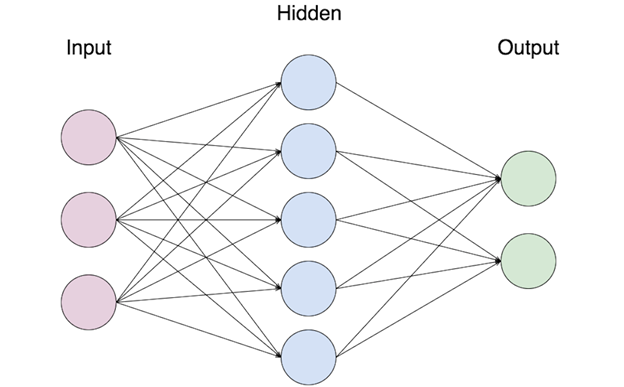
Artificial Neural Networks Structure
The very first layer is the input layer and the very last layer is the output layer; this output layer classifies our input using the information passed from all the layers before it. There can be x number of layers between the first and last and these are called hidden layers.
Between two layers, each neuron is connected to every other neuron which enables information to be passed between the layers. A neuron receives information in form of a number and it processes it before passing it to another neuron in the next layer, only if certain conditions are met (which we will go through later). This the network is based on the network of neurons found in the human brain.
 source https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/proxy/1*RGV6Bb3ChmVWsA8Q6Qth6Q.png
source https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/proxy/1*RGV6Bb3ChmVWsA8Q6Qth6Q.png
Neuron Activation
These neurons like the human counter part, processes the information it receives before passing on the information. As mentioned these neurons receive a number which is either passed from the input data (a pixel from a image) or the output from the previous layer. This number is usually set to be between 0 and 1.
The neurons between layers are connected by something called an edge and each of these edges has a weight assiocated with it. The weight represents the strenght of a particular neuron compared to others in that layer. These weights are original given a random value but it is updated via backpropagation based on the results of the cost function (we will cover this in another post). Each neuron has a bias value associated with it to allow for a neuron to be inactive, again it value is updated via backpropagation.
An activation in one layer determines the activation in the next layer and this activiation is based on a threshold where only if the threshold is meet, only then that particular neuron is activated and the information is passed on to the next layer.
An activation value is calculated using the input value, weights of the edges and the bias for that neuron. The formula is the sum of the inputs * weighted values plus the bias. This number will typically be larger than 1 so a non-linear activation function is used to scale this number down.
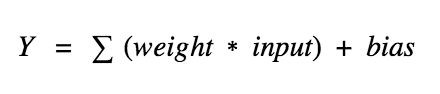 source https://miro.medium.com/max/440/1*vGj29ZBD1kH1kDlGQspPxA.png
source https://miro.medium.com/max/440/1*vGj29ZBD1kH1kDlGQspPxA.png
Activation Functions
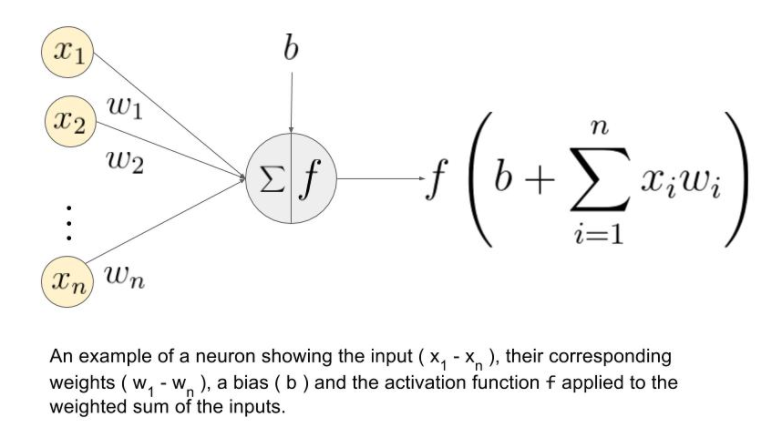
As mentioned the activation function is used to scale down a number of the activation value and there are a number of different functions to use.
 source https://miro.medium.com/max/766/0*yU8RsgJSeWnd2oL4.png
source https://miro.medium.com/max/766/0*yU8RsgJSeWnd2oL4.png
There is Sigmoid, Tan and ReLU out of which ReLU is one of the common ones used.
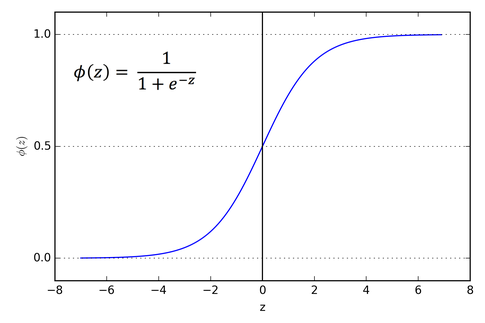
Sigmoid
Sigmoid scales the activation value to be between 0 and 1.
 source https://i.stack.imgur.com/czEqL.png
source https://i.stack.imgur.com/czEqL.png
Tan
Tan scales the activation value to be between -1 and 1.
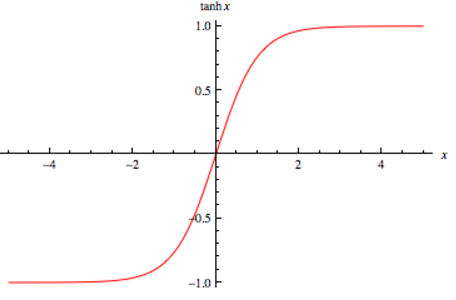 source https://i0.wp.com/sefiks.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/tanh.png?resize=456%2C300&ssl=1
source https://i0.wp.com/sefiks.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/tanh.png?resize=456%2C300&ssl=1
ReLU
ReLu scales the activation value to be between 0 and 1.
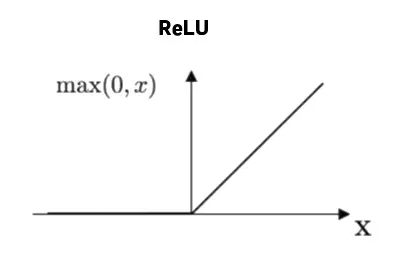 source https://i0.wp.com/highontechs.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/activation-functions3-3.jpg?resize=351%2C232&ssl=1
source https://i0.wp.com/highontechs.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/activation-functions3-3.jpg?resize=351%2C232&ssl=1
Once the activation value is passed through the function, this scaled number is compared to the threshold for that neuron to decided whether or not to pass the information on to the next layer. Then this continues for all neurons in all the layers to provide a final value for the output layer.
Why is neuron activation important?
It is important as only those active neurons pass on the information to the next layer and this means that neuron has found something of interest (this interest depends on the application). The activation function defines how the weighted sum of the input is transformed into an output from a node and as it is a non-linear transformation it can extract more information compared to not having any activation function (which effectively is just a linear function). With an activation function we will get the error and gradient which is needed for backpropagation to help the network learn better.
Next Post
This post will be a series of post to cover important concepts of a Neural Network such as Gradient Descent, Classification, Backpropagation.
